Discover the Power of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Not sure what which hyperbaric chamber is the best fit for you?
SCHEDULE A FREE CONSULTATIONLengthening Telomeres: Supporting cellular longevity and slowing the signs of aging.
Boosting Collagen Production: Enhancing skin elasticity and reducing the appearance of fine lines.
Reducing Immunosenescence: Revitalizing immune function for a healthier, more resilient body.
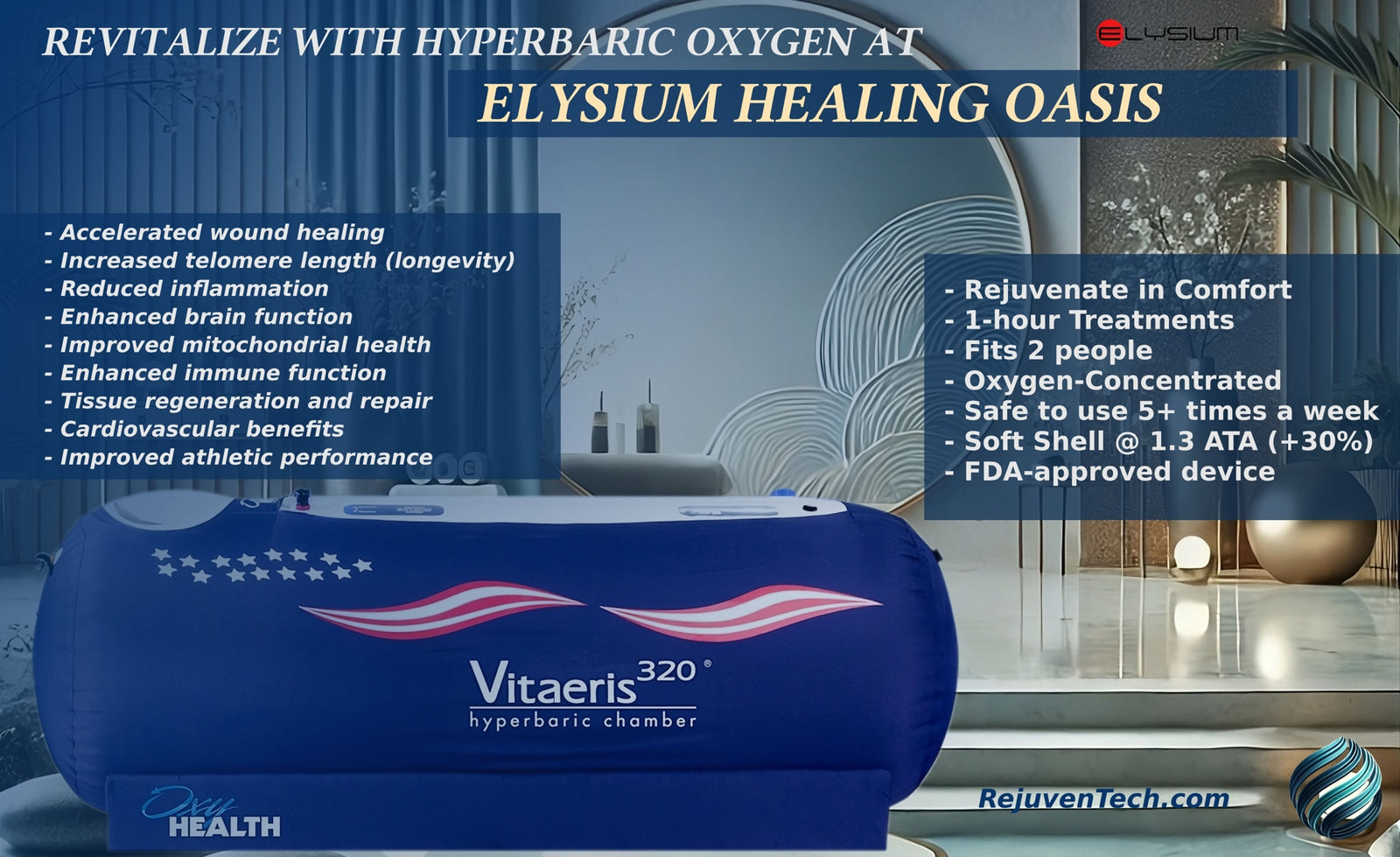
Speeds Up Tissue Repair
Enhances oxygen delivery to accelerate healing of wounds and injuries.
Reduces Inflammation
Decreases swelling and pain for faster recovery.
Boosts Immune Response
Fights infections and strengthens the immune system.
Industry-Leading Safety
OxyHealth chambers are trusted by professionals and families alike for their exceptional safety, exceeding federal standards and designed for lasting performance.
Proven Expertise
With 20+ years of innovation, OxyHealth delivers unmatched quality, combining expertise and superior design in every hyperbaric chamber.
Dedicated Support
OxyHealth offers outstanding customer care, with RejuvenTech as your personal representative for all inquiries, ensuring a seamless experience.
This is why we only carry OxyHealth products for your hyperbaric needs.
OxyHealth revolutionized hyperbaric therapy with safe, portable chambers trusted by physicians, athletes, wellness centers, and families.
Engineered for affordability, ease of use, and convenience, these chambers deliver effective therapy that has benefited hundreds of thousands worldwide.
Interested in renting a hyperbaric?
Every chamber undergoes rigorous inspections and is built to provide safe, reliable, and long-lasting functionality.
- Materials: Constructed in the U.S. with durable, non-toxic 44 oz. double-sided urethane and medical-grade components, ensuring durability and safety.
- Windows & Flanges: Single-mold windows and reinforced flanges deliver exceptional clarity, strength, and long-lasting seals.
- Internal Frame: Powder-coated steel frames maintain chamber integrity, ensuring convenience during entry and exit.
- Sealing: Advanced dielectric technology creates airtight seals without chemicals or glues for unmatched safety.
Integrating HBOT into your spa or clinic allows you to offer cutting-edge treatments that attract clients seeking innovative wellness solutions.
Whether you’re focusing on recovery, beauty, or general wellness, our range of hyperbaric oxygen chambers is tailored to meet diverse client needs.
Explore how HBOT can redefine the wellness experience and become a cornerstone of your professional practice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Hyperbaric Oxygen Chambers
-
Therapy (HBOT) involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, where the air pressure is 2 to 3 times higher than normal. This increased pressure allows your lungs to take in more oxygen than at normal air pressure, which promotes healing by helping fight infections and stimulating the release of growth factors and stem cells.
-
HBOT is used to treat a variety of medical conditions, including:
- Decompression sickness (a risk for scuba divers)
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Severe infections, including those caused by mold
- Non-healing wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers
- Radiation injuries
- Arterial gas embolism (air bubbles in blood vessels)
- Gangrene
- Crush injuries
It is also used for other conditions where tissues are deprived of oxygen.
-
Under high pressure in the chamber, oxygen is dissolved in the blood plasma and transported to areas where it is needed, even in damaged tissues with poor blood flow. This process helps reduce swelling, prevent tissue death, and fight infections. It also encourages the growth of new blood vessels, collagen, and skin cells, all of which are crucial for healing.
the following is an overview of the mechanisms by which HBOT works:
- Hyperoxygenation: Increased oxygen levels in the blood enhance tissue healing and reduce inflammation.
- Decrease gas bubble size: HBOT reduces the size of gas bubbles in the bloodstream, preventing damage to tissues and organs.
- Vasoconstriction: Increased oxygen levels cause blood vessels to constrict, reducing swelling and promoting healing.
- Angiogenesis: HBOT stimulates the growth of new blood vessels, improving tissue oxygenation and healing.
- Fibroblast proliferation/collagen synthesis: Increased oxygen levels promote the growth and activity of fibroblasts, leading to improved wound healing and tissue repair.
- Leukocyte oxidative killing: HBOT enhances the ability of white blood cells to kill bacteria and other pathogens.
- Reduced intravascular leukocyte adherence: Decreased adhesion of white blood cells to blood vessel walls reduces inflammation and promotes healing.
- Reduced lipid peroxidation: HBOT reduces oxidative damage to tissues and organs.
-
There are two main types of hyperbaric oxygen chambers:
- Monoplace Chambers: These are designed for a single person and resemble a long, clear plastic tube. The chamber is pressurized with 100% oxygen.
- Multiplace Chambers: These can accommodate several people at once. Patients receive oxygen through masks or hoods, and a technician may also be present in the chamber during treatment.
-
A typical HBOT session lasts from 45 minutes to two hours, depending on the condition being treated. You may feel a temporary fullness in your ears, similar to the sensation of being at high altitude or in an airplane, due to the increased air pressure. Swallowing or yawning can relieve this feeling. After the session, you might feel lightheaded or tired, but normal activities can generally be resumed immediately.
-
HBOT is generally safe, but it does come with some risks, including:
- Middle ear injuries due to pressure changes
- Temporary vision changes, like nearsightedness
- Lung collapse due to pressure changes (barotrauma)
- Seizures caused by oxygen toxicity
- Lowered blood sugar in people with diabetes
- Claustrophobia, fatigue, or headaches after treatment
In rare cases, serious complications like oxygen poisoning can occur, leading to seizures or lung problems.
-
The number of sessions required depends on the condition being treated. For instance, carbon monoxide poisoning may be resolved in three sessions, while non-healing wounds may require up to 40 sessions or more. HBOT is often part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes other therapies and medications.
-
Medicare, Medicaid, and many insurance companies typically cover HBOT for approved conditions, such as non-healing diabetic wounds, carbon monoxide poisoning, and decompression sickness. However, coverage may vary, so it’s important to check with your insurance provider to confirm coverage and whether pre-authorization is required.
-
HBOT is not suitable for everyone. People with certain conditions, such as recent ear surgery or injury, lung diseases, or those with colds or fevers, may need to avoid this treatment. Always discuss the potential risks and benefits with your healthcare provider before starting HBOT.
-
Before your session, you’ll be asked to wear a hospital-approved gown and remove any potentially flammable items, such as lighters or petroleum-based skincare products. Your healthcare team will provide specific instructions on how to prepare safely for the treatment.
-
- National average cost: $400
- Minimum cost: $45
- Maximum cost: $1,100
- Average range: $150 to $650
Total treatment cost (before insurance): $3,000 – $26,000
Please note that costs may vary depending on factors such as location, type of facility, condition being treated, and insurance coverage. It’s essential to consult with a hyperbaric oxygen therapy provider or clinic for a more accurate estimate of the cost for your specific situation.
**Last updated: August 2024
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has garnered attention for its potential anti-aging benefits, which extend beyond its traditional uses in wound healing and treating decompression sickness. Here’s an overview of the key anti-aging benefits of HBOT, supported by research:
1. Telomere Lengthening
- Benefit: One of the hallmarks of cellular aging is the shortening of telomeres, the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes. As cells divide, telomeres gradually shorten, leading to cellular aging and eventual cell death. HBOT has been shown to increase telomere length, which is associated with increased cellular longevity and a reduction in age-related diseases.
- Reference: A study published in the journal Aging found that HBOT significantly increased telomere length in blood cells by over 20% after a series of treatments, suggesting a potential reversal of aging at the cellular level .
2. Reduction of Immunosenescence
- Benefit: Immunosenescence refers to the gradual decline of the immune system associated with aging, leading to increased susceptibility to infections and chronic diseases. HBOT has been shown to decrease immunosenescence by increasing the production of circulating stem cells and improving the function of white blood cells, thus boosting the immune system's effectiveness.
- Reference: The same Aging study that demonstrated telomere lengthening also reported a reduction in immunosenescence, as evidenced by decreased levels of senescent cells and increased activity of stem cells .
3. Enhanced Collagen Production
- Benefit: Collagen is a critical protein that provides structure and elasticity to the skin. As we age, collagen production decreases, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin. HBOT has been shown to stimulate collagen production, which can improve skin elasticity and reduce the appearance of wrinkles, contributing to a more youthful complexion.
- Reference: Clinical studies have demonstrated that HBOT can enhance collagen synthesis, leading to improved skin elasticity and reduced signs of aging, as noted in research on skin aging and wound healing .
4. Antioxidant Upregulation
- Benefit: Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, is a significant contributor to aging. HBOT induces an adaptive response in the body, increasing the production of antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, thereby protecting cells from damage and slowing down the aging process.
- Reference: Research published in Redox Biology highlights how HBOT can upregulate antioxidant defenses, helping to mitigate oxidative stress and protect against age-related cellular damage .
5. Improvement in Cognitive Function
- Benefit: Cognitive decline is a common aspect of aging, often linked to reduced oxygen flow to the brain and the accumulation of oxidative damage. HBOT has been shown to enhance cognitive function by improving oxygen delivery to the brain, promoting neurogenesis, and reducing inflammation.
- Reference: A study in Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience found that HBOT improved cognitive function in aging patients, particularly in areas such as memory, attention, and executive function, by increasing cerebral blood flow and reducing neuroinflammation .
Conclusion
The anti-aging benefits of hyperbaric oxygen therapy are increasingly supported by scientific research, making it a promising intervention for those looking to slow down the aging process and enhance overall vitality. By promoting telomere lengthening, reducing immunosenescence, enhancing collagen production, upregulating antioxidants, and improving cognitive function, HBOT offers a multifaceted approach to healthy aging.
References
-
Hyperbaric oxygen chambers come in different types, each designed to serve specific therapeutic needs and environments. Below is an overview of the main types of hyperbaric oxygen chambers:
1. Monoplace Hyperbaric Chambers
- Description: Monoplace chambers are designed to accommodate a single person. The chamber is a long, cylindrical tube where the patient lies down on a bed that slides into the chamber. It is pressurized with 100% oxygen.
- Usage: These are commonly used in clinical and outpatient settings where individual therapy is needed. They are ideal for treating conditions such as chronic wounds, decompression sickness, and carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Advantages: Monoplace chambers are relatively compact, making them easier to install and maintain in smaller facilities. They also offer a controlled environment for delivering precise oxygen therapy.
2. Multiplace Hyperbaric Chambers
- Description: Multiplace chambers are larger and designed to accommodate multiple patients simultaneously, along with medical staff. These chambers are pressurized with air, and patients breathe 100% oxygen through masks or hoods.
- Usage: These are typically used in hospitals and larger clinics, especially when treating multiple patients at the same time, such as in emergency settings or for conditions that require close monitoring by medical staff.
- Advantages: Multiplace chambers allow for the treatment of several patients at once and enable medical personnel to enter the chamber to monitor and assist patients during the therapy. They are versatile and can be used for a wide range of conditions.
3. Portable Hyperbaric Chambers
- Description: Portable or inflatable hyperbaric chambers are smaller, lightweight, and designed for easier transportation and use in various settings, including homes. These chambers are pressurized with ambient air, and the patient breathes concentrated oxygen through a mask.
- Usage: These are often used for mild hyperbaric oxygen therapy (mHBOT) in non-hospital settings, including private practices, wellness centers, and homes. They are typically used for conditions that benefit from lower pressure treatments.
- Advantages: Portability and ease of use are the main advantages. They are less expensive and require less space compared to monoplace and multiplace chambers, making them accessible for personal use or in smaller facilities.
4. Veterinary Hyperbaric Chambers
- Description: These chambers are specially designed for animals, allowing veterinarians to administer hyperbaric oxygen therapy to pets and other animals. They are similar to monoplace chambers but are adapted to accommodate animals comfortably.
- Usage: Veterinary hyperbaric chambers are used to treat animals with conditions such as wounds, infections, and inflammatory diseases.
- Advantages: These chambers provide a safe and controlled environment for delivering hyperbaric oxygen therapy to animals, helping to accelerate healing and improve outcomes for various medical conditions.
5. Research Hyperbaric Chambers
- Description: These specialized chambers are used in research settings to study the effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy under controlled experimental conditions. They can be either monoplace or multiplace, depending on the study requirements.
- Usage: Research chambers are used by scientists and medical researchers to explore new applications for HBOT, develop new protocols, and investigate the physiological effects of hyperbaric oxygen exposure.
- Advantages: These chambers are equipped with advanced monitoring and control systems to allow precise data collection and analysis, which is essential for scientific research.
Each type of hyperbaric oxygen chamber serves specific needs and environments, ranging from individual patient care to research and even veterinary applications. The choice of chamber depends on factors such as the number of patients, the conditions being treated, space availability, and whether the treatment setting is clinical, research-based, or at home.
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy provides numerous health benefits that can attract a wide range of clients. HBOT is known to enhance healing by increasing oxygen levels in the body, which accelerates tissue repair and reduces inflammation. It is particularly beneficial for conditions like chronic wounds, sports injuries, and post-surgical recovery. Additionally, HBOT is gaining popularity in the wellness industry for its potential anti-aging effects, as it promotes cellular rejuvenation, boosts the immune system, and improves overall vitality. Offering HBOT can differentiate your business and attract clients seeking advanced therapeutic options.
-
The space required for a hyperbaric oxygen chamber varies depending on the type and size of the chamber. Monoplace chambers, which accommodate a single person, generally require around 6-8 feet in length and 3-4 feet in width. Multiplace chambers, which can hold multiple clients, will need significantly more space. It’s essential to also consider room for associated equipment, such as oxygen tanks and control panels, as well as adequate ventilation and access for clients and staff. The space should be easily accessible, with enough room for safe entry and exit from the chamber.
-
The initial cost of purchasing a hyperbaric oxygen chamber can range from $50,000 to $200,000 or more, depending on the size, type, and features of the chamber. Monoplace chambers are typically less expensive than multiplace chambers. In addition to the purchase price, businesses should budget for ongoing maintenance costs, which include regular inspections, servicing of the oxygen delivery system, and replacing any worn parts. The cost of oxygen supply is another consideration, as well as ensuring compliance with local regulations regarding the storage and use of medical-grade oxygen.
-
Safety is a top priority when offering HBOT, as it involves the use of pressurized oxygen, which can present risks if not properly managed. It is essential to follow all safety guidelines, including proper training for staff, regular maintenance of the chamber, and strict protocols for client use. Businesses must also comply with local and national regulations, which may include obtaining specific licenses or certifications to operate a hyperbaric oxygen chamber. It’s advisable to have emergency procedures in place and to ensure that the chamber is monitored by qualified personnel during sessions.
-
Marketing HBOT requires a focus on education and awareness, as many potential clients may not be familiar with the therapy's benefits. Highlight the specific health and wellness benefits of HBOT in your marketing materials, such as its effectiveness in speeding up recovery, reducing inflammation, and promoting overall health. Offering introductory sessions or packages can encourage clients to try the therapy. Additionally, leveraging testimonials from satisfied clients, creating informative content (such as blog posts or videos), and collaborating with healthcare professionals to validate the benefits can help build trust and attract a broader client base. Consider targeting specific groups, such as athletes, post-surgical patients, or those interested in anti-aging treatments.
-
All HBOT chambers, whether medical-grade or non-medical, must comply with FDA regulations, local safety codes, and operational best practices. Proper infrastructure, including adequate space and ventilation, is essential for safe operation.
-
While not legally required in most states, completing the 40-hour introductory hyperbaric medicine course is highly recommended. This training ensures your team is well-versed in safety, operational standards, and patient management. Details are available here.
-
No. All HBOT services require a licensed physician to oversee treatments, even under general supervision. This ensures compliance with medical and legal standards and guarantees patient safety.
-
Under general supervision, a physician does not need to be on-site but must:
- Train and oversee staff.
- Maintain responsibility for the chamber and treatments.
- Document their role for every session.
-
Accreditation, such as from the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS), is optional but demonstrates a commitment to high industry standards. Accreditation can enhance client trust and business credibility.
-
Businesses should implement comprehensive safety protocols, including:
- Regular maintenance of hyperbaric chambers.
- Detailed emergency response plans.
- Staff training to address risks and operational challenges.
-
The choice depends on your business goals. Medical-grade chambers (2.0 ATA and above) are ideal for FDA-approved treatments and medical practices such as wound healing, mold toxicity recovery, and the bends, while non-medical chambers are suited for wellness-focused businesses offering recovery and anti-aging therapies.
-
Bennett MH, Mitchell SJ. Hyperbaric and Diving Medicine. In: Jameson J, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, et al., eds. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 20th Edition. McGraw Hill; 2018.
Heyboer M III, Sharma D, Santiago W, et al. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Side Effects Defined and Quantified. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2017; 6(6): 210-224. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5467109/. Accessed January 7, 2023.
Kranke P, Bennett MH, Martyn‐St James M, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for chronic wounds. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015; 6. https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD004123.pub4/full. Accessed January 9, 2023.
LeGros T, Murphy-Lavoie H. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. In: Tintinalli JE, Ma O, Yealy DM, et al., eds. Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 9th Edition. McGraw Hill; 2020.
Olson KR. Oxygen and Hyperbaric Oxygen. In: Olson KR, Anderson IB, Benowitz NL, et al., eds. Poisoning & Drug Overdose, 7th Edition. McGraw Hill; 2018.
Ruotsi LC. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. In: Hamm RL, ed. Text and Atlas of Wound Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition. McGraw Hill; 2019.
Undersea & Hyperbaric Medical Society. Indications for Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. January 7, 2023.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Get the Facts. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/hyperbaric-oxygen-therapy-get-facts. Accessed January 7, 2023.
Bennett MH, et al. Emerging indications for hyperbaric oxygen. Current Opinions in Anesthesiology. 2019; doi:10.1097/ACO.0000000000000773.
Mechem CC, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed September 14, 2020.
Moghadam N, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in sports musculoskeletal injuries. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2019; doi:10.1249/MSS.0000000000002257.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Don't be misled. September 14, 2020.
Shields RC (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. September 25, 2020.
Melnyczenko AR (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. September 25, 2020.
-
Facilities offering medical-grade chambers (2.0 ATA and above) must ensure FDA compliance, meaning the chamber must be cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or hold an approved investigational device exemption. Additionally, adherence to local and state fire safety codes is required to meet regulatory and operational standards.
-
Yes, supervising physicians must:
- Hold an unrestricted medical license in their practicing state.
- Be board-certified in a primary medical discipline (recommended).
- Complete a 40-hour introductory hyperbaric medicine course, strongly recommended for understanding the unique operational and medical needs of medical-grade chambers. Learn more here.
- Maintain current Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) certification to manage potential emergencies.
-
Under general supervision, physicians are not required to be on-site during medical-grade hyperbaric treatments. However, they remain responsible for:
- Training non-physician staff.
- Maintaining equipment and supplies.
- Documenting their supervisory role for every session (e.g., 'Hyperbaric oxygen therapy was performed under my overall direction and control.').
-
Medical-grade chambers operate at higher pressures (2.0 ATA and above) and are designed for FDA-approved medical uses. They offer advanced safety features, superior construction, and precise oxygen delivery compared to non-medical chambers, which typically operate at lower pressures and may not meet stringent medical standards.
-
Technicians administering treatments in medical-grade chambers should complete a 40-hour hyperbaric medicine course, covering patient management, safety protocols, and operational training. This ensures competence in handling the advanced features of a 2.0 ATA chamber. Find details about this course here.
-
While not mandatory, obtaining Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS) accreditation is highly recommended. This certification demonstrates adherence to the highest industry standards for safety, quality, and medical efficacy.
-
Facilities must regularly maintain and inspect medical-grade hyperbaric chambers, ensure emergency response plans are in place, and train all staff in operational and safety procedures specific to 2.0 ATA chambers.
For businesses
Medical-Grade Hyperbaric Oxygen Chambers

Easily Disable 5G on Your Phone for Health and Longevity (Android)
Unfortunately, newer Android models like the Samsung S25 have removed easy access to disable 5G from the standard settings menu. But the method shown here circumvents that limitation and gives you full control of your device's network connection in a few free, easy steps.

Natural Remedies to Remove Neurospora Sitophila Mold from the Body
Neurospora sitophila is a red/orange mold that can colonize the body, particularly the sinuses and brain, leading to chronic inflammation, neurological symptoms, and respiratory distress. Removing it requires a comprehensive natural approach that includes antifungal treatments, sinus cleansing, detoxification, immune support, and environmental control.

Brain Health as the Ultimate Success Multiplier, Part 5: How Successful People Can Proactively Safeguard Their Health
Success isn't a product of willpower and ambition alone—it requires a strong foundation of physical and mental well-being. Yet, many high achievers only begin prioritizing their health after encountering burnout, cognitive decline, or unexplained fatigue. The good news? Health deterioration is often preventable, and brain function can be optimized with the right strategies.

Brain Health as the Ultimate Success Multiplier, Part 4: The Multiple Health Assaults That Hinder Potential
While ambition, talent, and discipline are essential components of success, they can only go so far when the body and brain are under attack. Numerous health assaults, often unnoticed or underestimated, silently chip away at the potential of even the most driven individuals. These assaults don't just cause occasional fatigue or brain fog—they can derail entire careers, diminish creative capacity, and leave otherwise capable people struggling to perform at their peak. Understanding these hidden health disruptors is crucial for anyone seeking long-term success.